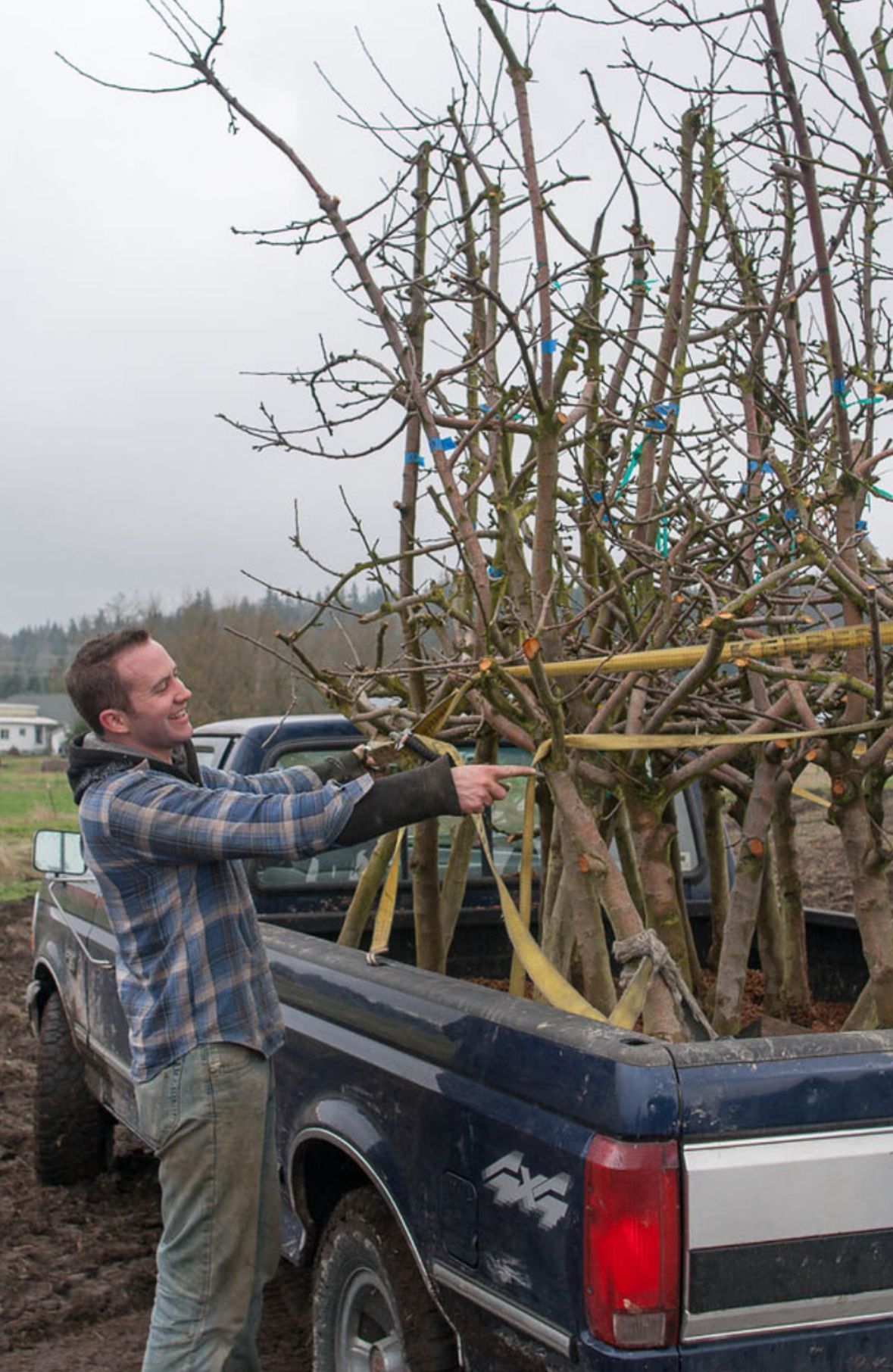
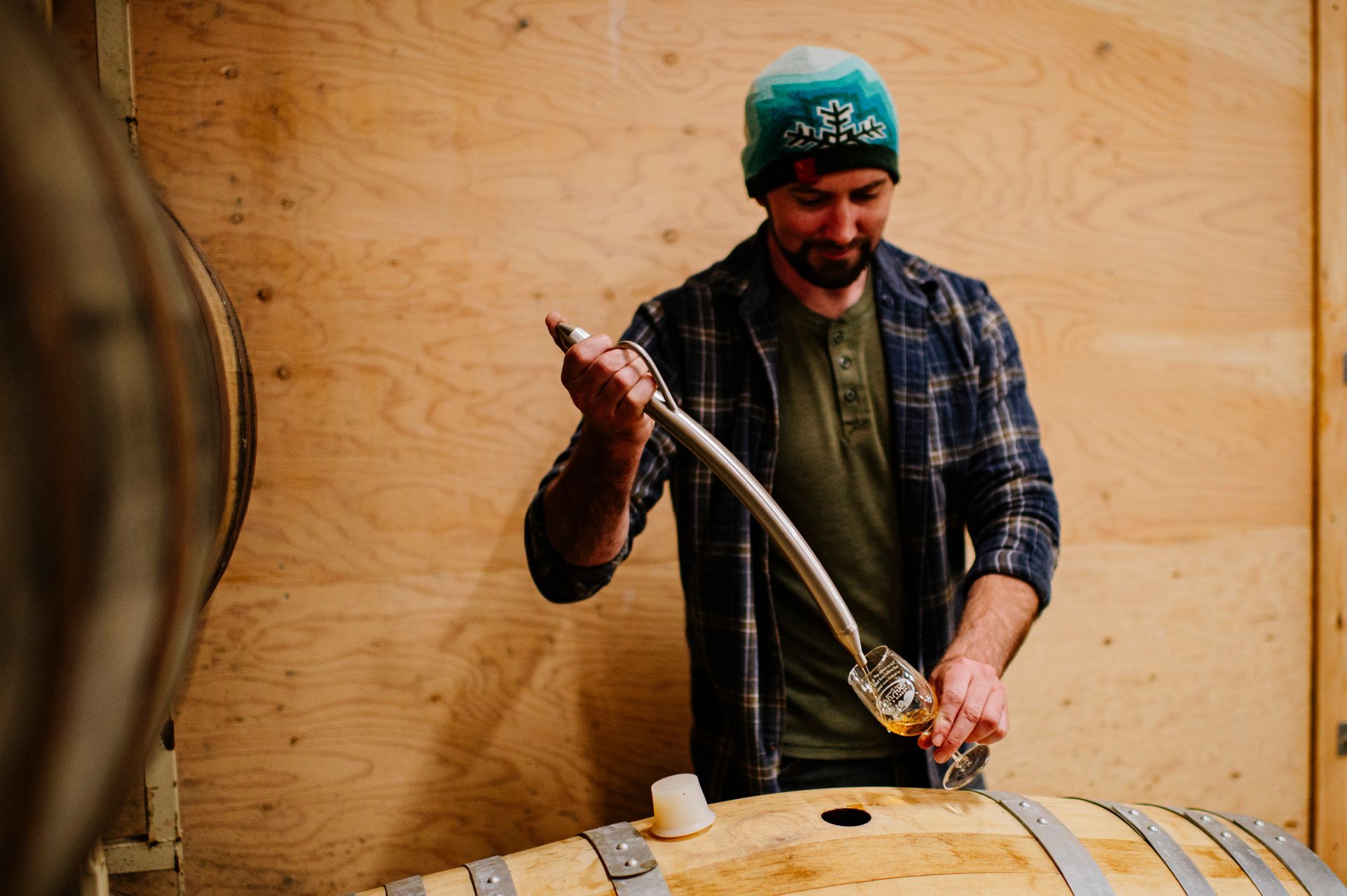
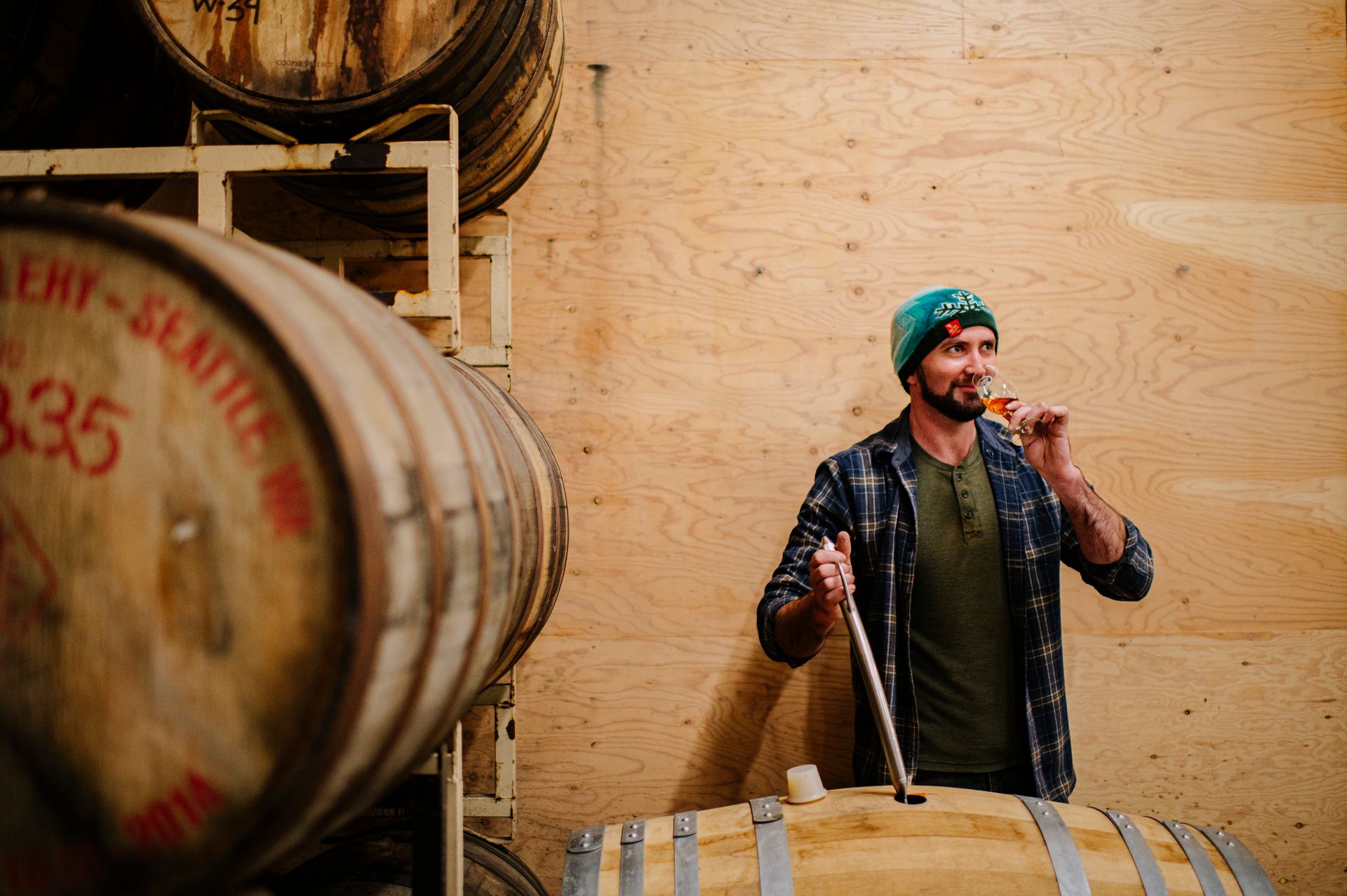
Finnriver Cidermaker Chris Weir has experimented with barrel aging cider for over a decade, starting from his early days at Finnriver. His barrel aging journey began with Fire Barrel, crafted with a blend of seven cider apple varieties aged in barrels. Finnriver acquired both the original recipe and the trees for this cider in the winter of 2013 from Drew Zimmerman, who was retiring from his Red Barn cider operation in the Skagit Valley. Chris was part of the crew that dug up all 1,000 trees, 19 varieties of cider apples, and then drove them back to Chimacum where they were planted in our current organic orchard (photo at left shows Chris in 2013 with a truckload of the trees they transplanted). This deep-rooted experience has shaped Chris’ expertise and passion for barrel aging and the story has come full circle as Chris is now barrel-aging cider made from those same trees.
After working for Finnriver as a young cidermaker, Chris went to make wine in California for several years before returning to WA to work as a brewer and then head cidermaker for another cider company before returning to Finnriver two years ago. Along the way, he experimented with barrel aging wine, beer and cider. He shares, “Wine is more stable in a barrel since it has a higher ABV. In my experience, cider is the most challenging. With a lower ABV it isn’t as shelf stable and requires a little more babying. We have to check on them regularly and keep them topped off. It is a meticulous process that requires regular monitoring to ensure the cider develops the desired flavors without compromising its stability.” Chris prefers the gradual infusion of flavors from barrel aging over some other methods, like using wood chips. "I like being able to taste it as it ages and remove the oak right when it hits the point I want. It’s a fine line to walk."